Summary
- Profile Type
- Technology offer
- POD Reference
- TOES20231220006
- Term of Validity
- 11 January 2024 - 10 January 2026
- Company's Country
- Spain
- Type of partnership
- Research and development cooperation agreement
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
- Targeted Countries
- All countries
Contact the EEN partner nearest to you for more information.
Find my local partner
General information
- Short Summary
- A Spanish university has developed an innovative system warning the presence of an object/individual close to a certain area by emitting an acoustic/light signal. The device is able to receive an electrical signal from a conductive cement-based material which acts as an electrical switch when pressure is applied on it. It has multiple applications in civil infrastructures intelligent sensorisation. Companies interested in acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation are sought.
- Full Description
-
Multifunctional cementitious conductive materials consist of concrete, mortars and pastes containing conductive fibers or particles (usually based on carbon or metals) that increase the electrical conductivity of the final material to make it viable for the development of new applications.
Among the interesting technical features of conductive cementitious materials, the following stand out: the perception of deformation, the perception of structural damage, electromagnetic wave shielding, thermal insulation (room heating or frost protection), electrochemical chloride removal, cathodic protection, etc.
The perception of the deformation of a material is understood as the change in the unit variation of the electrical resistivity in volume, which is proportional and reversible to the stress to which it is subjected. If the applied stress is compressive, the electrical resistance in longitudinal direction decreases. On the other hand, if the stress is tensile, it increases in a similar way. In the elastic regime, both responses are reversible, so that the electrical resistance recovers its initial value when the applied stress ceases. This effect, in the case of conductive cementitious materials, could be applied for structural or load control (vehicles or people).
For the perception of deformation to be of sufficient magnitude and reversible, the addition of electrically conductive particles to the cementitious matrix is necessary. In this case, it is not necessary for the added material to form a continuous conductive path through the material for strain sensing to be effective
In this senste, a Spanish university has developed a device capable of receiving an electrical signal from a conductive cement-based material (pastes, mortars and concretes) which, due to changes in electrical resistivity when pressure is applied, pre-amplifying and transforming it, allows the cementitious material itself to act as an electrical switch.
With the measurement of the deformation of the cementitious material, new applications can be developed, including, for example, providing the traffic network of a city with smart materials that warn drivers that a pedestrian is approaching a sidewalk with the intention of crossing the road (Smart City concept).
In this sense, a switch system has been developed that warns of the presence of an object and/or individual close to a certain area by emitting an acoustic and/or light signal.
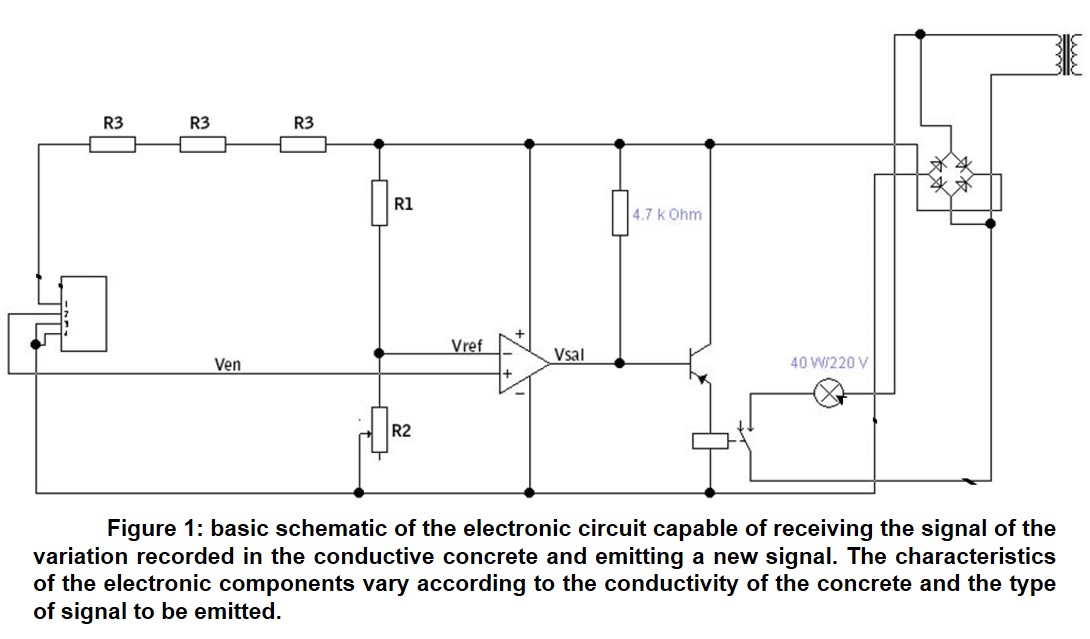
This switching system (see Figure 1) consists of, at least:
• A sensor whose electrical resistance changes when subjected to mechanical stress or strain.
• A cementitious composite consisting of cement, aggregates, water, additives, and a hybrid mixture of carbon nanotubes and expanded graphite that is configured to provide the first electrical output signal in response to the deformation of the material in which it is contained, whose signal is a function of the variation of the electrical resistivity of the material itself.
• Two electrical electrodes distributed in levels or layers within the same sensor, which are electrically powered from a power supply source of direct current electrical energy at a constant intensity.
• An electronic evaluation circuit that receives the first electrical output signal and provides as output, a warning signal to the target object and/or individual.
• Two evaluating electrodes distributed in a stacked configuration in levels or layers arranged between two layers adjacent to electrical electrodes, which are electrically connected to the evaluating electronic circuit.
• A comparator amplifier that receives the first electrical output signal and a reference electrical signal (from a reference electronic circuit) that provides a second electrical output signal.
Manufacturers of smart sensors and or multifunctional conductive cementitious materials interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation through utility model licensing agreements are sought. - Advantages and Innovations
-
ADVANTAGES OF THE TECHNOLOGY
The main advantage of this invention is the practical implementation of the theoretical concepts based on the perception of the deformation or piezoresistivity of cement-based materials with addition of carbonaceous materials with conductive properties.
This innovative device is characterized because it is sustainable and environmentally friendly.
INNOVATIVE ASPECTS OF THE TECHNOLOGY
The object of the present invention combines previous knowledge regarding the manufacture of cement-based materials (capable of sensing their own deformation) with electronic devices capable of making feasible the practical use of this property.
To date, no device has been found on the market that can transform the variation in the electrical properties of the material into a signal capable of being implemented in a practical application.
This innovative device allows multiple applications related to the development of smart sensors in civil infrastructures, such as:
• Switching on streetlights when vehicles or people pass by.
• Activating acoustic and/or light signals in the event of dangers (pedestrian crossings, over-heavy vehicles, etc.).
• Modifying the sequencing of traffic lights according to the flow of vehicles.
• Activate safety systems installed in traffic lanes.
Thanks to the development of electronic devices for the reception and transformation of the signal received as a result of the variation in the electrical properties of the material, it is possible to subsequently use it as an open/closed circuit in different practical applications.
These applications are included in the Smart City concept. - Stage of Development
- Lab tested
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Not relevant
- IPR status
- IPR applied but not yet granted
- IPR notes
- Spanish utility model application but not yet granted.
Partner Sought
- Expected Role of a Partner
- Acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation
- Type and Size of Partner
- SME 11-49
- SME 50 - 249
- SME <=10
- Big company
- Type of partnership
- Research and development cooperation agreement
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
Dissemination
- Technology keywords
- 002006008 - Sensory/Multisensory Technology, Instrumentation
- 09001009 - Sensor Technology related to measurements
- 002006001 - Building Materials, Components and Methods
- 02006001 - Materials, components and systems for construction
- 005006006 - Sensors/Multisensor Technology, Instrumentation
- Market keywords
- 009007002 - Manufacture of building materials
- 09007002 - Manufacture of construction materials, components and systems
- 09007004 - Engineering and consulting services related to construction
- 01004006 - Other data communication components
- Targeted countries
- All countries