Summary
- Profile Type
- Technology offer
- POD Reference
- TOES20231220003
- Term of Validity
- 11 January 2024 - 10 January 2026
- Company's Country
- Spain
- Type of partnership
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
- Research and development cooperation agreement
- Targeted Countries
- All countries
Contact the EEN partner nearest to you for more information.
Find my local partner
General information
- Short Summary
- Two Spanish universities have developed plant cell cultures (Morus genus) to obtain stilbenes by simultaneously using two elicitor compounds to promote their production. High quantities of trans-resveratrol and trans-oxyresveratrol can be obtained, which could be used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries due to their powerful antioxidant capacity. Companies interested in acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation through patent licensing agreements are sought.
- Full Description
-
Stilbenes are biologically active phenolic compounds with a broad spectrum of antibiotic and pharmacological activity. However, the production of this group of compounds in nature is restricted to a small number of plant species such as grapevine (Vitis sp.) mulberry (Morus sp.) or peanut (Arachis hypogaea), as an adaptive mechanism in response to stress (UV irradiation, microbial infection, exposure to heavy metals or ozone treatment). Within this group of compounds (stilbenes), trans-resveratrol (hereinafter t-resveratrol), piceatanol and trans-oxyresveratrol (hereinafter t-oxyresveratrol) are of particular note.
t-Resveratrol and piceatanol are found in grapevine and peanut, while t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol are found in mulberry, indicating that stilbene synthesis is species-dependent.
Epidemiological and laboratory studies have shown that stilbenes in general, and t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol in particular, have favourable health effects, making their inclusion in the human and animal diet desirable.
t-Resveratrol is very effective in the prevention and therapy of atherosclerosis, as an anti-inflammatory agent and as an anti-hyperoxidative agent, while t-oxyresveratrol is notable for its pharmacological properties as an anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective, antibiotic and antiviral agent, as well as exhibiting potent tyrosinase inhibitor activity, which gives it interesting cosmetic properties.
Given the beneficial role of t-oxyresveratrol on human and animal health, it is important to have a suitable biological source to obtain it.
The stimulation of stilbene synthesis has been explored with a variety of "elicitor" type compounds, such as pieces of fungal cell walls, cyclodextrins, methyl jasmonate, etc.
The combined treatment of these elicitors produces a synergistic effect in grapevine cell culture. However, there is very little knowledge on how to produce t-oxyresveratrol.
With current knowledge, the production of t-oxyresveratrol by biotechnological means requires the implementation of two processes:
a) On the one hand, the production of mulberroside A (double glycosylated form of t-oxyresveratrol) using mulberry (Morus alba) cell cultures elicited with salicylic acid, followed by extraction and purification.
b) On the other hand, the bioconversion of mulberroside A into t-oxyresveratrol by enzymatic treatment.
In order to solve the biotechnological problems described above, it is necessary to have a more efficient method for obtaining t-oxyresveratrol in a single process.
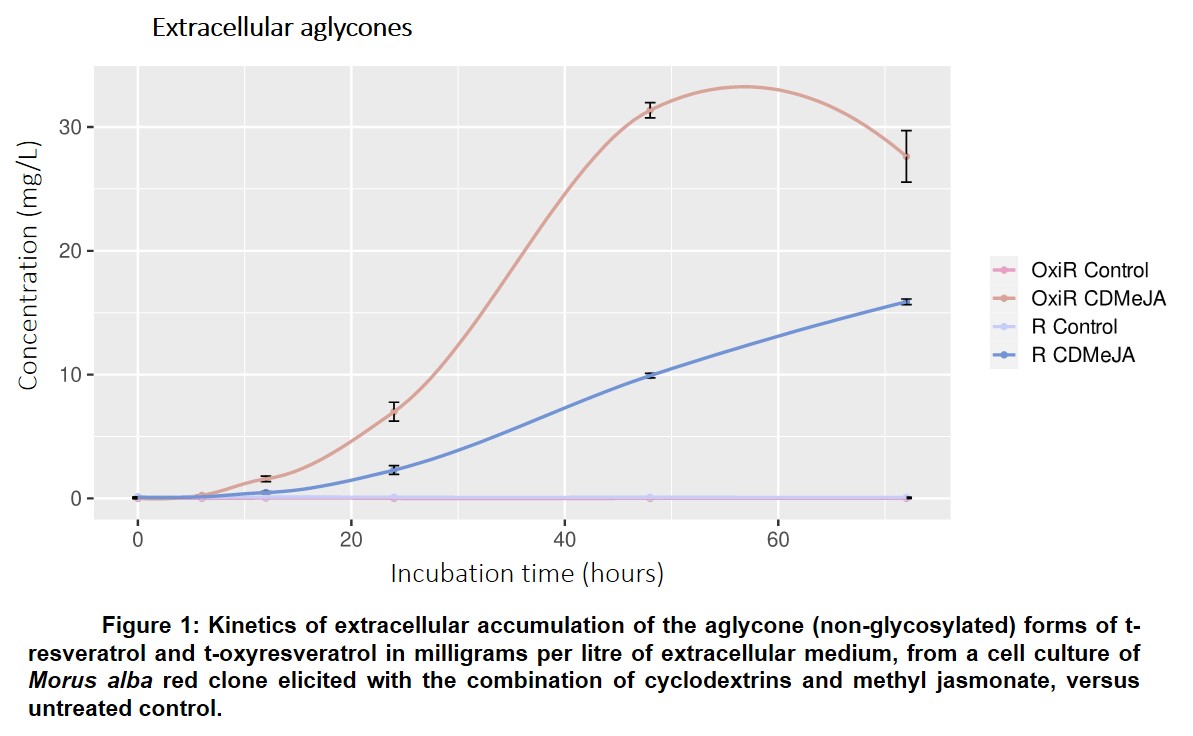
In this sense, two Spanish universities have developed a method to obtain stilbenes by the combined addition of cyclodextrins and methyl-jasmonate to a culture medium of plant cells of the genus Morus. Specifically, large extracellular quantities of t-reveratrol and, above all, t-oxyresveratrol are obtained (see Figure 1).
Any cell line of a plant of the genus Morus is capable of producing these compounds, either naturally or after genetic modification.
The method of production comprises the following steps:
1) Addition of cyclodextrins and methyl-jasmonate to a culture medium of plant cells of the genus Morus.
2) Incubation of the cell culture medium obtained in the previous step.
3) Separation of t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol (obtained in step 2) from the culture medium.
4) Purification of the t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol separated in the previous step.
This technology can be applied to the pharmaceutical, cosmetics, food and nutraceutical sectors.
Companies interested in acquiring this technology for commercial exploitation through patent licensing agreements are sought. - Advantages and Innovations
-
The developed method has the following advantages:
1) It is more efficient than current biotechnological methods.
2) It is carried out in a single process, which simplifies the production process.
3) The accumulation of t-resveratrol and t-oxyresveratrol is mostly extracellular.
4) The extraction and purification process is simplified (no need to break the plant cells and then remove the cellular remains).
5) It is possible to use the plant cells in suspension for new t-resveratrol and t-oxysveratrol synthesis cycles.
6) The trans- forms of both compounds (which are the biologically active forms, as opposed to the cis- isomers) are mainly generated.
7) High amounts of stilbenes are obtained:
• In the red clone: 124 mg/L t-oxyresveratrol; 24 mg/L t-resveratrol.
• In the white clone: 114 mg/L t-resveratrol; 81 mg/L de t-oxyresveratrol.
8) t-Oxyresveratrol and t-resveratrol production is stable and independent of environmental and socio-economic factors.
9) The quality of the final product is improved.
10) The process is sustainable and environmentally friendly.
11) The technology allows large quantities of stilbenes to be obtained at a lower cost than other similar techniques currently available on the market, which increases its accessibility for different industrial applications.
INNOVATIVE ASPECTS OF THE TECHNOLOGY
Surprisingly and unexpectedly, the combined use of cyclodextrins and methyl jasmonate in plant cell cultures of the genus Morus results in the production of two stilbenes not anticipated in the state of the art, namely t-resveratrol and, especially, t-oxyresveratrol.
The cumulative concentrations of both stilbenes are higher in the combined treatment than the sum of the individual treatments, hence the synergistic effect of both elicitors.
The accumulation of both stilbenes occurs mostly in the extracellular medium, which simplifies the extraction and purification process and reduces production costs. - Stage of Development
- Lab tested
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Not relevant
- IPR status
- IPR applied but not yet granted
- IPR notes
- Spanish patente application but not yet granted.
Partner Sought
- Expected Role of a Partner
- Acquiring this technology for its commercial exploitation.
- Type and Size of Partner
- SME 11-49
- SME 50 - 249
- SME <=10
- Big company
- Type of partnership
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
- Research and development cooperation agreement
Dissemination
- Technology keywords
- 06002002 - Cellular and Molecular Biology
- 06001019 - Stem cell Technologies
- 06002001 - Biochemistry / Biophysics
- Market keywords
- 007003004 - Food supplements/vitamins
- 08001023 - Other chemicals and materials (not elsewhere classified)
- 05007002 - Pharmaceuticals/fine chemicals
- 07003002 - Health food
- Targeted countries
- All countries