Summary
- Profile Type
- Technology offer
- POD Reference
- TOCH20241127008
- Term of Validity
- 27 November 2024 - 27 November 2025
- Company's Country
- Switzerland
- Type of partnership
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
- Research and development cooperation agreement
- Targeted Countries
- All countries
Contact the EEN partner nearest to you for more information.
Find my local partner
General information
- Short Summary
- A Swiss university offers an oxygen sensor. Besides being robust, the sensor excludes interference from other gases and has a high sensitivity over a large concentration range. Possible applications: exhaust gas analysis, air quality measurements, early detection of food spoilage, breath monitoring, fire protection sensors in oxygen-free facilities like server rooms, monitoring oxygen free production processes like metal 3D printing. Licensing agreements with manufacturer of gas sensors sought.
- Full Description
-
State-of-the-art oxygen sensors suffer from various drawbacks when it comes to achieving high sensitivity. Trade‑offs are typically made to achieve a high sensitivity: high-temperature resistive sensors have a large energy consumption whilst analytical instruments such as spectrometers have a complex build. Colorimetric sensing probes are also single‑use only.
The Swiss university offers a low-cost, highly sensitive, robust, multi-use oxygen sensor, which operates over a broad range of oxygen concentrations, while avoiding cross-influence from other gases.
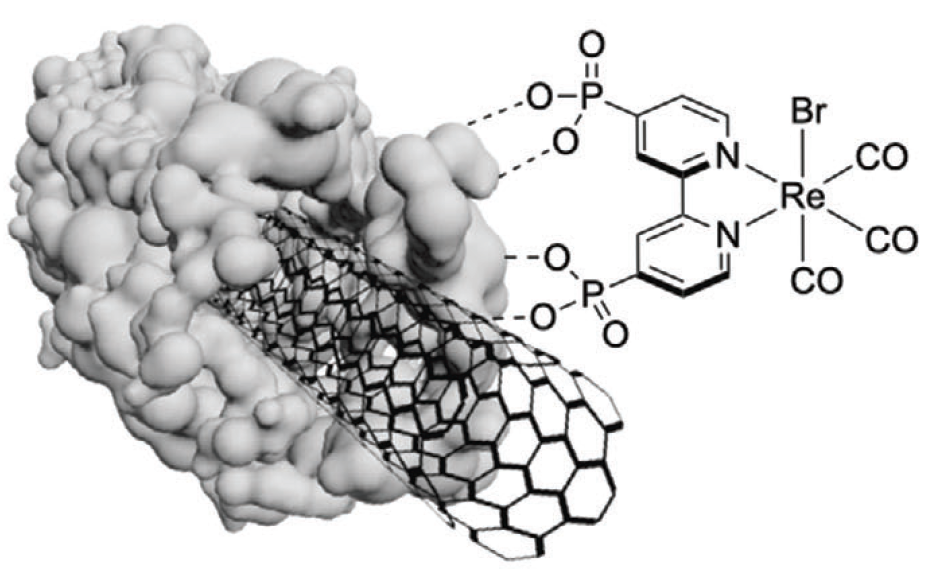
The core component of the sensor is a composite made of carbon nanotubes and titanium oxide. During a measurement the electric resistance of the composite is recorded. The selectivity and sensitivity of the sensor towards a specific gas, i.e. oxygen, is tailored by coating the composite with a photosensitizer. The photosensitizer is activated by green light, for example from a photodiode. In the presence of green light electric charges will hop from the photosensitizer to the composite and change its resistance. In the presence of green light and oxygen the charge is trapped by the oxygen and does not reach the composite. The presence of oxygen, thus, reduces the charge transfer to the composite and reduces the change in electric resistance. There is a linear dependence between changes in oxygen concentration and changes in the electrical resistance of the sensor.
Technical specifications
• Sensitivity: Detects O₂ level changes in the ppb (parts per billion) range, with fast response and recovery.
• Selectivity: High specificity for O₂, with minimal interference from N2O, CO₂, H₂, CH₄, as well as C2H4 and CO.
• Robustness: Operates consistently across a temperature range from -50°C to 200°C and humidity levels up to at least 80%.
• Low power consumption: Operating well below 0.6W
• Low detection limits: Achieves sub-ppm (parts per million) detection, ideal for sensitive environments.
Potential applications
• Environmental and food spoilage monitoring: Suitable for detecting low O₂ levels in air, water and food packaging quality control, even in remote settings.
• Medical and biological monitoring: Useful for cellular health and hypoxia detection where precise O₂ control is essential.
• Fire protection in controlled environments: Effective for nitrogen-flushed server rooms to prevent fire by maintaining low O₂ levels.
• Industrial manufacturing: Ideal for oxygen-free processes like metal 3D printing, where minute O₂ levels impact quality.
This sensor offers strong market potential due to its efficient, low-cost, and compact design. Potential industry partners in manufacturing, environmental science, and healthcare may benefit through licensing or collaborative R&D for tailored applications.
Fig. 1 shows a schematic of the sensor: Single-walled carbon nanotubes are covered with titania (TiO2) A Rhenium complex acts as the photosensizer. It is attached to the composite via the titanium coating.
Reference: "A Dye-Sensitized Sensor for Oxygen Detection under Visible Light", Adv. Sci. 2024, 2405694 https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202405694 - Advantages and Innovations
-
• Low power consumption (< 0.6W) and compact design: suitable for portable applications
• Low-cost and compact design: scalable for mass production
• High sensitivity and high selectivity: covers applications where the detection of trace amounts of oxygen is crucial, such as 3D metal printing
• High robustness: fits applications in environments where unexpected interferences may occur such as a sudden increase in humidity - Stage of Development
- Available for demonstration
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Goal 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- IPR status
- IPR applied but not yet granted
Partner Sought
- Expected Role of a Partner
-
The sought partner is a manufacturer of gas sensors, specifically oxygen sensors.
Tasks to be performed by the partner sought:
The sought partner has own R&D resources to push the development of the sensor towards a market ready product. A research collaboration is possible for the joint prototype development. The partner will license the technology from the Swiss university. - Type and Size of Partner
- SME 11-49
- Big company
- SME 50 - 249
- Type of partnership
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
- Research and development cooperation agreement
Dissemination
- Technology keywords
- 06001005 - Diagnostics, Diagnosis
- 10002008 - Measurement and Detection of Pollution
- 08002001 - Detection and Analysis methods
- 09001009 - Sensor Technology related to measurements
- 3D printing
- Market keywords
- 05005007 - Pulmonary medicine
- 06001007 - Other oil and gas
- 03001009 - Other electronics related (including keyboards)
- Targeted countries
- All countries