Summary
- Profile Type
- Technology offer
- POD Reference
- TODE20240724019
- Term of Validity
- 12 August 2024 - 12 August 2025
- Company's Country
- Germany
- Type of partnership
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
- Research and development cooperation agreement
- Targeted Countries
- All countries
Contact the EEN partner nearest to you for more information.
Find my local partner
General information
- Short Summary
- A German Start-up has developed sustainable and lightweight CubeSat structures made of the high-performance polymer PEEK using injection molding. Compared to conventional aluminum structures, production time, costs and use of resources are reduced. Other advantages are a lower mass, better corrosion resistance, improved damping capacity and lower CO2 emissions. Partners sought are aerospace companies that want to integrate the technology or R&D partners to further improve it.
- Full Description
-
Small Scale Satellites are crucial for New Space as they have made access to space and its commercial use relatively easy and affordable. CubeSats, that represent more than 90% of all launched nanosatellites, usually consist of an Aluminium Frame to withstand the harsh conditions of space.
However, the production of Aluminium is very energy-intensive and the material is potentially harmful to the environment when being disposed. And although aluminium is already relatively light, the use of even lighter materials offers further potential for optimization so that a heavier payload can be carried.
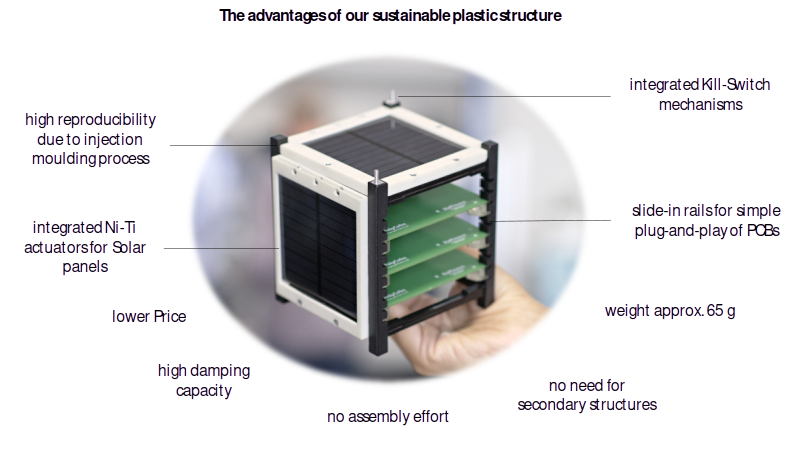
A German SME that emerged from an established plastics supplier for the automotive industry has developed an injection molding tool that produces a CubeSat structure and components from space-qualified material. The aluminium frame is replaced by PEEK (Polyether ether ketone), a high-temperature-resistant, thermoplastic, semi-crystalline high-performance plastic that can be used as a substitute for metal. The manufacturing processes have been proven in the automotive industry.
The PEEK structure is at least 20 percent lighter than comparable aluminum structures. The production and disposal of PEEK compared to aluminum leads to a significantly lower environmental impact. Integrated automated and ultra-lightweight unlocking mechanisms (pin pullers) based on shape memory alloys (SMA) make the structure particularly practical. SMA can be used for various Hold-Down and Release Mechanisms, such as unlocking antenna or solar modules.
The company is now looking for satellite manufacturers who would like to integrate the company’s innovative plastic structures and the shape memory actuators into their products to be used in commercial or scientific missions. Also, manufacturers of satellite systems that are seeking the customized development and production of satellite components by plastic injection moulding and 3D printing are suitable partners. Partnerships sought are commercial agreements with technical assistance.
Moreover, the company wants to further improve the product, for instance by integrating bio-polymers or recycled materials suitable to be used in space. Suppliers of smart or sustainable materials might be partners for joint R&D projects contributing to the qualification of sustainable materials for use in space. - Advantages and Innovations
-
• Cost reduction: use of material and production process are more cost-effective compared to conventional cube sats
• Lower weight: Replacing aluminium with PEEK enables weight savings of up to 20 %. This results in fuel savings, a factor of utmost significance for your mission costs.
• Energy savings and reduced CO2 emissions: The production of aluminum requires more energy than the production of plastics. The extraction and processing of aluminum from bauxite ore involve significant energy inputs, while this value diminishes, particularly with recycled plastics. This has the potential to reduce CO2 emissions by up to 80%.
• Zero waste: Defective products or materials wasted during the process are recycled and reused, undergoing shredding and melting for a new purpose, while this is not as straightforward with leftover aluminum chips due to the milling process.
• Better End-of-Life Disposal: Plastics can burn more quickly during re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere and therefore pollute our atmosphere less than metals, the residues of which (metal oxides) remain in the atmosphere, with the negative effects of this currently being researched.
• Better corrosion resistance
• Improved damping capacity
• Shape memory alloys (SMA) in the structure allow for practical unlocking mechanisms. ideal for space applications due to its unique weight specific working capacity - Stage of Development
- Lab tested
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Goal 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Goal 13: Climate Action
- IPR status
- Secret know-how
Partner Sought
- Expected Role of a Partner
-
• Satellite manufacturers, operators of commercial or scientific space missions or satellite / IoT networks: Integration of the CubeSat Structures into missions
• Manufacturers of satellite systems: Joint technological development of customized components using injection molding and 3D printing
• Scientific organizations or companies as R&D partners: Joint R&D projects to further improve the technology, for instance by integrating bio-polymers - Type and Size of Partner
- R&D Institution
- SME 11-49
- Big company
- Other
- SME 50 - 249
- SME <=10
- University
- Type of partnership
- Commercial agreement with technical assistance
- Research and development cooperation agreement
Dissemination
- Technology keywords
- 01006008 - Satellite Technology/Positioning/Communication in GPS
- 06006002 - Bioplastics
- 02007014 - Plastics, Polymers
- 02007019 - Lightweight materials
- 02011005 - Space Exploration and Technology
- Market keywords
- 01005005 - Other satellite/microwave
- 01005004 - Microwave and satellite components
- 08001018 - Polymer (plastics) materials
- Sector Groups Involved
- Energy-Intensive Industries
- Aerospace and Defence
- Targeted countries
- All countries